JEIO TECH, established in South Korea in 1989, is a leading provider of high-precision laboratory equipment and scientific instrumentation.

Over the past few years, the South Korean industry has endured a series of supply-chain disruptions, encompassing shortages arising from the COVID-19 pandemic and Japan's restrictions on the export of semiconductor materials in 2019. Consequently, the Korean government and industry have prioritized the establishment of an independent and resilient supply chain on a national scale. From a macroscopic standpoint, what is your evaluation of the strengths of the South Korean industry, and what challenges does it confront? And how crucial do you consider the development of a robust SME sector for the South Korean industry to achieve a strong supply chain in Korea?
In 2020, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, we encountered numerous challenges related to material and equipment procurement. For instance, the cost of semiconductor equipment, which would typically be valued at 3000 KRW, skyrocketed to 300,000 KRW. At times, we had to sell products at a loss because of the scarcity of chip manufacturers in the domestic market, forcing us to explore all available options.
We are acutely aware of the limited availability of indigenous materials and equipment. When it comes to logistics and cost-effectiveness, we face strong competition from other players because of our heavy reliance on sourcing parts from overseas. South Korea's core strength historically lay in delivering high-quality finished goods compared to international competitors. The conglomerates you mentioned achieved their current status primarily by prioritizing the production of high-quality products and services.
The Korean government has been actively supporting the establishment of a domestic supply chain, particularly following Japan's unilateral export control measures in 2019. My company has also secured government funding for the manufacturing of bio-pharmaceutical equipment. More recently, the South Korean government has introduced initiatives and provided support for research and development efforts. The aim is to shift our focus from simply procuring low-cost materials to acquiring materials that can perform exceptionally well under ultra-extreme weather conditions. Tomorrow, I will be attending a meeting to discuss an establishment of a national testing institution as a council member. This institution will spearhead research into materials capable of functioning effectively in extreme weather conditions.
In summary, South Korea's remarkable achievements have been built upon a strong focus on finished goods. Similarly, many SMEs tend to prioritize finished products. However, it is regrettable that SMEs haven't taken a more proactive role in researching and developing materials suitable for their good quality finished goods.

JEIO TECH Headquarters, Daejeon city, South Korea
Critics argue that the country's large corporate conglomerates have grown to such immense size and diversity that they obstruct the emergence of a robust SME sector. In support of their contention, journalists often highlight the fact that while Korean SMEs have a strong track record of serving domestic conglomerates, they encounter challenges in attracting international clients. Do you concur with this argument? Secondly, your company has achieved significant international success. What, are the competitive advantages that have enabled you to successfully venture beyond the borders of South Korea?
Perhaps in the past, this argument held some truth. Korean SMEs may have lacked sophisticated marketing skills, which made them heavily reliant on large conglomerates, who couldn't always guarantee consistent profits or margins for the SMEs. However, recent trends have shown a shift in this dynamic. Korean bio companies, for instance, have expanded their focus beyond just serving domestic pharmaceutical giants to target multinational bio companies, potentially yielding greater profits. I believe SMEs can enhance their corporate value through well-planned marketing strategies of their own, rather than relying on specific buyers such as venturing into overseas market, for instance.
As for JEIO TECH, in lab business, we are supplying complete products to a diverse range of customers rather than to certain companies. From the early stage of this company, we have been trying overseas business through collaboration with foreign distributors. As a result, we are able to reduce our dependency on certain companies.
Examining our industry structure, it's interesting to note that the sector is predominantly dominated by German and large U.S. companies. German companies typically specialize in specific areas and then market their products globally. However, since Korean and other Asian companies entered the global arena later, we have had to diversify our range of product categories. Presently, the product categories from Korea, Japan, and China are broader in scope. One of our significant advantages lies in our one-stop supply chain, facilitated by our direct logistics channel. We serve as a single provider where clients can procure all the various items they need without the hassle of dealing with multiple entities.
Another strength of Korea lies in its sophisticated electronics industry, largely spearheaded by conglomerates such as LG and Samsung. They have already established a fertile groundwork for us, allowing us to benefit from their efforts and maintain a competitive edge over our counterparts.

JEIO TECH Laboratory Showroom
In recent years, there has been significant interest in testing medical equipment to combat the spread of diseases like COVID-19. However, there are also emerging areas of research that are experiencing increased demand, such as regenerative medicine, genomics, and cell biology. Looking ahead over the next five to ten years, what do you anticipate will be the new applications for your products, and where do you expect the demand to come from?
While I may not be an expert in specific application fields, I believe that the demand for biomedicine is on the rise, as opposed to synthetic medicine. Consequently, there is a growing need for facilities capable of manufacturing biomedicine. Many laboratory equipment pieces can also serve as bio manufacturing equipment simultaneously. One critical requirement is that we must adhere to GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) standards, which include ensuring data integrity.
One significant trend in the laboratory equipment sector is the increasing connectivity of equipment and the utilization of digital technologies to obtain more accurate data and extend the lifespan of equipment. Your company introduced LC Connected back in 2017, which created a remote monitoring system for lab equipment. How do you harness digital technologies to offer more competitive products to your customers?

LC Connected (Mobile Monitoring System)
Currently, the functions remain relatively basic, such as monitoring enabled by devices. However, the term "digital twin" has gained prominence in the lab equipment field. Nonetheless, we are still at the early stages of implementing more advanced functions. Although we may not offer these services directly, there are companies that specialize in providing comprehensive information services related to all digital data within their laboratories. Sometimes, demonstrating how much and how long you utilize your equipment to your maintenance provider is crucial, especially since maintenance contracts in the U.S., for instance, often include these elements.
During my visits to various labs with customers, I have noticed an interesting aspect. You mentioned that German companies tend to specialize in a single product and export it internationally. However, when you enter a laboratory, you often encounter test chambers, X-rays, shakers, and stirrers, each from different brands. Is there not a compatibility issue? In such cases, would it not be advantageous to establish a common maintenance standard?
In the past, certain companies pursued a closed ecosystem approach, which ultimately proved unsuccessful. Consequently, companies are now opening their APIs to other firms to facilitate better communication. A noteworthy example is Europe's initiative to establish standardized protocols for various laboratory equipment, known as LADS. This protocol is built upon the OPC UA Industry 4.0 framework, aiming to create a standard protocol for inter-device communication among different laboratory equipment. As lab equipment becomes increasingly automated, inter-device communication is becoming more critical than ever, prompting efforts to establish standardized protocols in Europe.
JEIO TECH was established in 1989, and one of the distinctive features of your company is the total solutions you offer. Your versatility extends to both large-scale equipment and precision devices, making your offerings unique. Could you provide a historical overview of JEIO TECH and highlight some of the key milestones and technical accomplishments of the company?
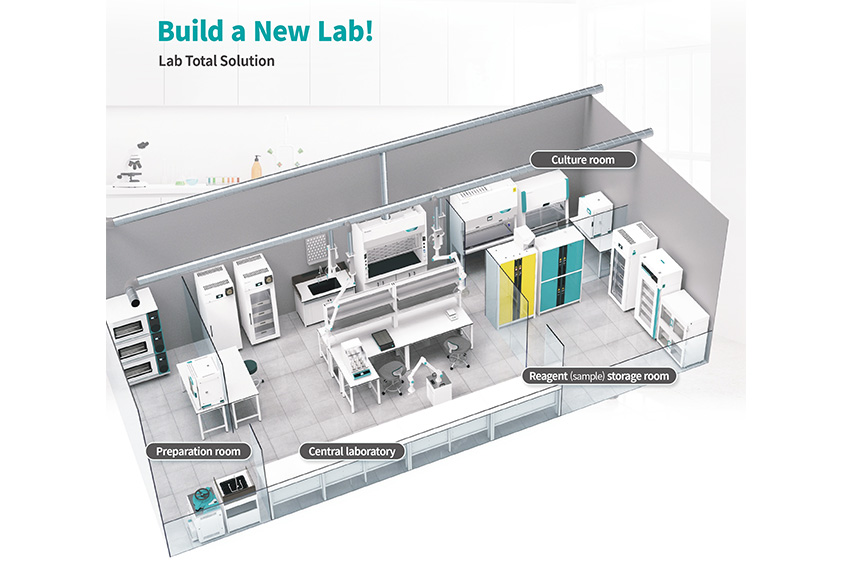
JEIO TECH Lab Total Solution
Initially, the founder of JEIO TECH held a Ph.D. in organic chemistry and came from a family with a background in running a plant. While examining the equipment in factories, the founder wondered why there were no indigenous or locally developed experimental equipment, with most of it being sourced from overseas markets. This sparked two ambitions: first, the desire to develop homegrown equipment, and second, the aspiration to gradually change the reliance on overseas-sourced equipment. This led to the gradual expansion of our product offerings. Furthermore, we have placed a strong emphasis on safety equipment. In the past, many Korean companies producing safety equipment did not adhere to safety standards and specifications, whereas we aimed to follow international standards. As a result, we develop and manufacture most of our products in accordance with international standards such as fire safety storage cabinet that adhere to EU standards as an example.
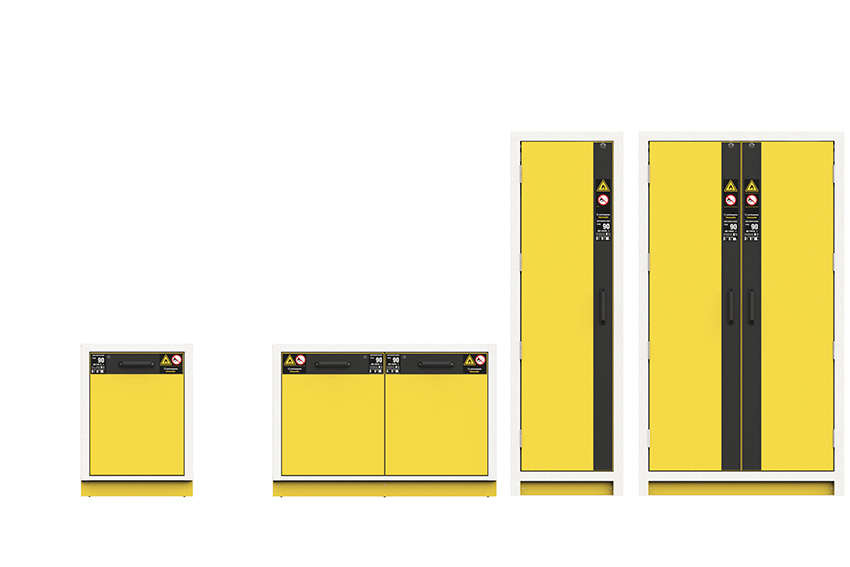
JEIO TECH Fire Safety Storage Cabinet
As previously mentioned, our laboratory equipment serves not only laboratory needs but can also be used in biomedical manufacturing facilities. Additionally, we continually provide laboratory equipment for industrial purposes behind the scenes, driven by such demands.
JEIO TECH boasts a diversified product portfolio catering to various industries, including molecular biology, biotech, medical and genetic research, and clinical science. The company has also expanded its product range to include industrial solutions, such as test equipment, serving industrial sectors like semiconductors and general chemistry. Looking ahead, which applications or industries are you looking to expand into, and where do you see the highest growth potential?
One of our core focuses is the secondary battery testing equipment sector, which is experiencing significant demand. The equipment used in secondary battery production closely resembles that of the semiconductor manufacturing process. Given South Korea's status as a semiconductor powerhouse, we are considering entering the semiconductor sector as well.
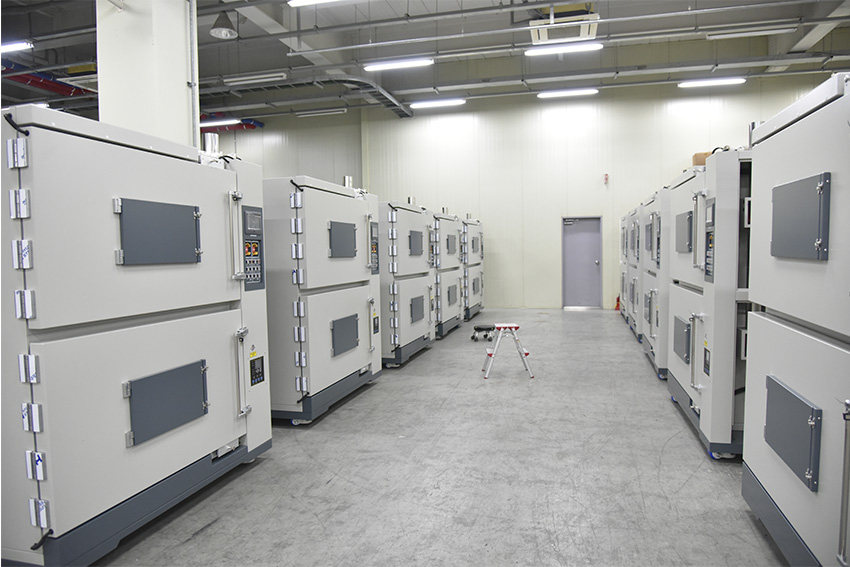

Battery Test Chambers, manufactured in JEIO TECH
The secondary battery sector has garnered considerable attention in the media, with discussions revolving around deeper integration between the American, Japanese, and Korean supply chains to reduce reliance on China for critical materials. Recently, South Korea's new president visited the U.S. to sign a series of treaties aimed at providing Korean firms with U.S. government assistance when selling materials and equipment. How is this influencing your business, and is the U.S. market your primary focus for the battery market?
Due to the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), an increasing number of Korean companies are seeking to relocate their plants to the U.S. Given that equipment inevitably entails maintenance requirements, we are also considering focusing on this aspect. Fortunately, we have a U.S. branch near Boston, which enables us to respond to demand better and more promptly in the U.S. market.
Are you currently seeking partnerships, either in terms of technological development or distribution?
JEIO TECH recognized the strong need for collaboration in order to create innovative value. Recently, we are engaged in research and development activities with a research institute. Engaging in discussions with various groups allows us to foster creative thinking and acquire valuable insights to address challenges.
In addition to technical aspects, we are also collaborating with distribution partners, both in our domestic market and international markets. Over 35 years of our history, we have established excellent partnerships with various distribution channels. Such collaborations offer the potential for mutually beneficial results. As our business model continues to evolve, we are actively seeking distribution partners in new business sectors.
JEIO TECH has built an international network comprising more than 300 distributors and dealers worldwide. Additionally, the Lab Companion brand has established a presence in overseas branches located in China, Malaysia, the UK, and North America. Can you provide insight into your international strategy? Which international markets will you prioritize for future growth, and where do you see the highest growth potential?
It can be challenging to pinpoint specific regions for priority focus. The lab equipment market is largest in the U.S., followed by Europe and China, all of which certainly demand our attention. Simultaneously, we are keenly interested in Southeast Asia, India, and the African continent, where rapid industrial development is occurring. Rather than fixating on a particular region, we believe it's essential to conduct detailed analyses to determine which products hold greater appeal in specific areas. This approach enables us to identify demand and assess the competitiveness of our product range, which is quite extensive. Promoting all our products in a single market can be daunting.
In countries like Korea, the U.S., and Europe, which are developed economies with strong infrastructure and reliable electricity supplies, clients are well-versed in operating and maintaining our equipment. However, in less developed regions like China, Southeast Asian countries, or African nations, local workforces may purchase the equipment but lack the knowledge to operate and maintain it. As you expand into these developing economies, how important is client education? Will you provide counseling or after-sales services?
Thankfully, we have distributors in several major African countries who offer comprehensive services, covering not only sales but also technical support. Our business and equipment are highly valued by them, and they are deeply invested in providing such services.
If I were to return to meet you on the last day of your presidency at JEIO TECH, is there a specific goal or ambition you would like to achieve during your tenure as president?
In the long term, my aspiration is to ensure the utmost satisfaction of all our employees, surpassing their expectations. I envision creating a workplace so appealing that not only our employees but even their offspring aspire to work for our company in the future.

For more details, explore their website at: https://www.jeiotech.com/eng/
And their social media:
JEIOTECH Blog: https://www.jeiotech.com/eng/news/blog.php
JEIOTECH Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/@jeiotech
JEIOTECH Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/jeiotech.eng
JEIOTECH Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/company/jeiotech/mycompany/?viewAsMember=true
0 COMMENTS